11 Secrets You Need To Know For Exponential Growth

Here’s a Silicon Valley secret you need to know. Rapid success of startups has nothing to do with luck and everything to do with a new breed of organizational structure, which allows massive impact with a very small footprint.
I call them the Exponential Organizations, or ExOs.
ExOs are creating 10 times more impact than their peers in the same industry at record-breaking speed. Even more incredulously, they’re doing it with less investment and fewer people than traditionally ever thought possible.
After identifying and researching over 100 ExOs to find out what they’re doing to rapidly scale, I distilled 11 specific attributes which any company can adopt to deliberately engineer exponential results.
This article provides an overview of these 11 attributes which allow existing organizations or startups to rapidly scale and achieve exponential results.
The 11 Attributes of ExOs
The ExO framework consists of the Massive Transformative Purpose (MTP) as a foundation upon which the remaining 10 attributes stand on. These 10 attributes are further divided into five external characteristics and five internal mechanisms, for which the acronyms SCALE and IDEAS are used respectively.
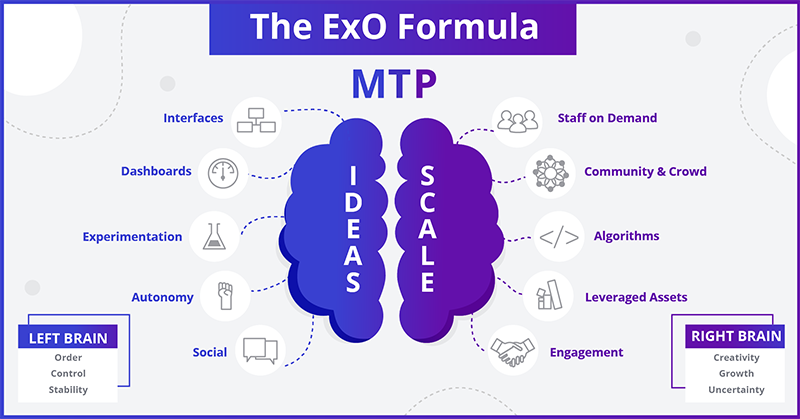
Part 1: MTP Foundation
#1 Massive Transformative Purpose
In Short
This is your “why”. It’s what motivates you. It’s what drives a community who share the same vision around you.
A Massive Transformative Purpose (MTP) describes a better future for the world (or at least your industry or community). It doesn’t specify how. It’s not about you, your customers, your organization, your products or services. No ‘you’, ‘we’ or ‘us’. You are not in the picture. It is not a marketing slogan.
It is your north star, but it doesn’t restrict your organization from changing direction. It might excite and scare you, and catch in your throat, it matters that much to you.
You might never fully achieve it, yet it is still worth striving for. A great MTP attracts the customers, community, partners and resources you need to make a dent in the universe.
ExO Example
TED had been operating since 1984 as a high-end conference in Monterey limited to about 1,000 attendees. In 2001, Christopher Anderson’s non-profit Sapling Foundation acquired TED, and Anderson became its Curator.
Enthralled by the quality of speakers, top minds and dreamers at TED, Anderson drove TED forward under the MTP, “Ideas worth spreading."
Driven by this MTP, he made two radical decisions.
First, he releases all the TED talks for free. Secondly, he allows anybody to create TEDx events. As a result, the first publicly-released TED talk achieved 1,000,000 views in less than three months. Today, TED talks are approaching 4 billion views globally and TED events have grown exponentially.
In just 5-6 years, with virtually zero cost, Anderson had created a global media brand and phenomenon; an achievement previously unheard of.
How It Contributes To Exponential Results And Growth
A strong MTP is an ExO’s competitive edge. It is so inspirational, it generates a cultural movement around the ExO, ultimately creating its own community, tribe and culture.
Here are some other examples of strong MTPs from ExOs:
- Google: “Organize the world’s information.”
- X Prize Foundation: “Bring about radical breakthroughs for the benefit of humanity.”
- Quirky: “Make invention accessible.”
- Singularity University: “Positively impact one billion people.”
In next week’s article, we will dive deeper into MTPs.
Part 2: SCALE
The external attributes of an ExO organization, SCALE, stands for:- Staff on Demand
- Community & Crowd
- Algorithms
- Leveraged Assets
- Engagement
#2 Staff On Demand
In Short:Minimize full-time staff. Outsource tasks.
ExO Examples:
Gigwalk relies on half a million smartphone-enabled workers. When Proctor and Gamble needs to know how and where its merchandise is being placed on Walmart shelves around the world, it can use Gigwalk’s platform to instantly deploy thousands of people who are paid a few dollars to walk into Walmart and check the shelves. Results come in within an hour.
How It Contributes To Exponential Results And Growth:
During the industrial revolution, having a large workforce allowed an organization to accomplish more. In today’s information age, that same large workforce becomes an anchor that reduces maneuverability and slows you down.
In any information-enabled business a large internal staff seems increasingly unnecessary, counterproductive and expensive. Outsourcing whenever you can makes your company agile, flexible, fast-moving, and cost-effective.
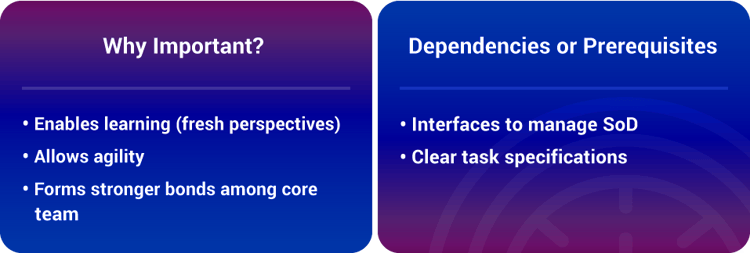
#3 Community & Crowd
In Short:If you build communities and you do things in public, you don’t have to find the right people — they find you.
ExO Examples:
Two well-known examples of ExOs leveraging crowds for funding are Kickstarter and Indiegogo. In 2012 there was an estimated $2.8 billion raised via crowdfunding campaigns. The World Bank predicts crowdfunding to grow to $93 billion by 2025.
How It Contributes To Exponential Results And Growth:
Today, the internet has made it possible for organizations to build their community and crowd beyond borders who share the same MTP.
ExOs leverage community and crowd for many functions traditionally handled inside the enterprise, including idea generation, funding, design, distribution, marketing and sales. This agility allows for rapid implementation and exponential results.
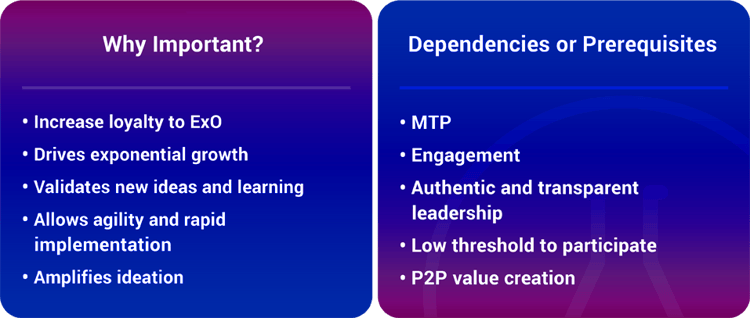
#4 Algorithms
In Short:
ExOs leverage data and algorithms to scale in ways that weren’t possible even 5 or 10 years ago.ExO Examples: Given that the 55,000 trucks in UPS’ American fleet make 16 million deliveries daily, the potential for inefficient routing is enormous. By applying telematics and algorithms, UPS saves its drivers 85 million miles a year, resulting in annual savings of $2.55 billion.
How It Contributes To Exponential Results And Growth:
Remarkably, and often tragically, most companies today are still driven almost solely on the intuitive guesses of their leaders who are just as likely to fall prey to a long list of self-delusions and cognitive biases.
Algorithms are thus a critical future component of every business. Almost all the business insights and decisions of tomorrow will be data-driven. Given that they are much more objective, scalable, and flexible than human beings, they are also critical for organizations committed to driving exponential growth.
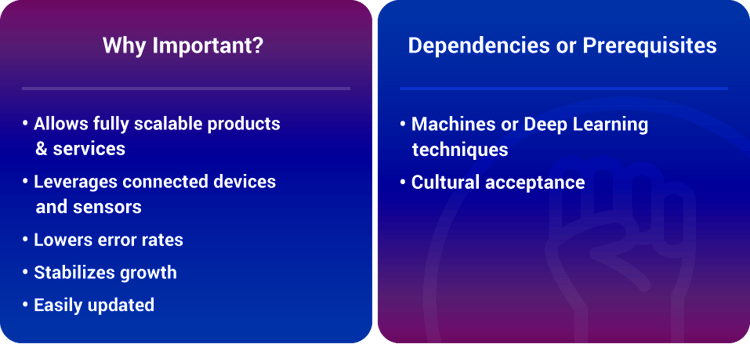
#5 Leveraged Assets
In Short:Hold on to what’s absolutely critical. Outsource everything else.
ExO Examples:
It took AirBnB just 10 years to become a $25 billion company and the world’s largest hotel chain without owning a single property. Waze piggybacked off its users’ smartphones to create a GPS navigational tool without ever needing to research and develop a handheld GPS.
How It Contributes To Exponential Results And Growth:
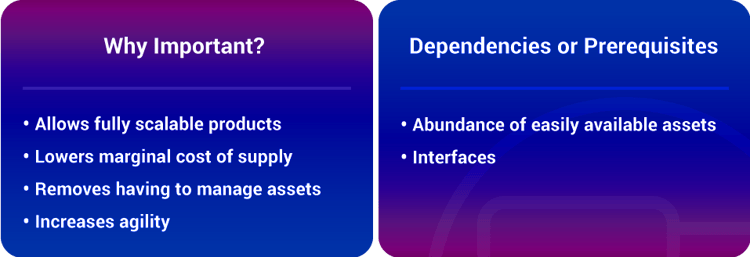
Renting, sharing or leveraging assets — as opposed to owning them — enables organizations to easily share and scale assets not only locally, but also globally, and without boundaries.
As with Staff on Demand, ExOs retain their flexibility precisely by not owning assets, even in strategic areas. This practice optimizes flexibility and allows the enterprise to scale incredibly quickly as it obviates the need for staff to manage those assets.
#6 Engagement
In Short:
Enabling collaborative human behaviour (social behaviour) to engineer the results you want from your community.ExO Examples:
Sweepstakes, quizzes, coupons, airline miles and loyalty cards have been around for a long time. But in the last few years, such techniques have been fully information-enabled, elaborated and socialized.
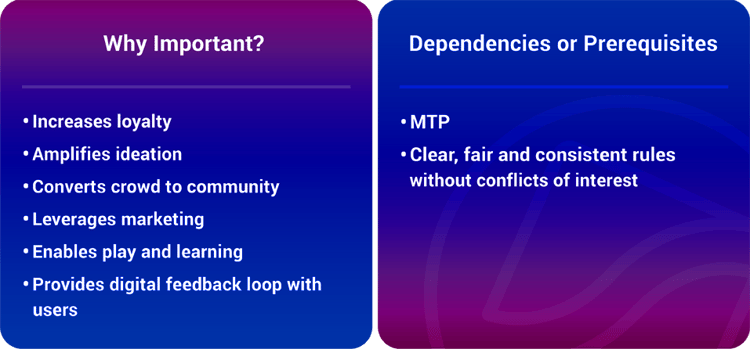
ExOs today engage through digital reputation systems, games and incentive prizes. All of these provide opportunity for virtuous, positive feedback loops — which in turn allows for faster growth due to more innovative ideas and customer and community loyalty.
Companies like Google, Airbnb, Uber, eBay, Yelp, GitHub and Twitter all leverage different engagement mechanisms across social media and other outreach platforms.
How It Contributes To Exponential Results And Growth:
Connected individuals can now do what once only large centralized organizations could. Engagement creates network effects and positive feedback loops with extraordinary reach.
The biggest impact of engagement techniques is on customers and the entire external ecosystem. However, these techniques can also be used internally with employees to boost collaboration, innovation and loyalty.
Unless an ExO is able to optimize the engagement of its community and crowd, it will wither and fade.
Part 3: IDEAS
The internal mechanisms of an ExO organization, IDEAS, stands for:- Interfaces
- Dashboards
- Experimentation
- Autonomy
- Social Technologies
#7 Interfaces
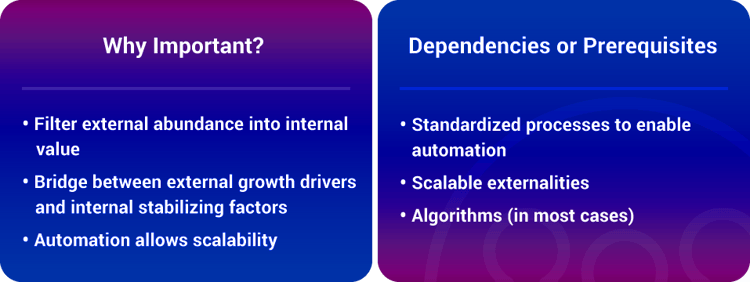
In Short:ExOs have very customized processes for how they interface with customers and other organizations. An example of this is Apple's strict rules on what reaches its app store.
ExO Examples: Google’s AdWords, a multi-billion dollar business within Google, is another classic example. A key to its scalability is self-provisioning — that is, the interface for an AdWords customer has been completely automated such that there is no manual involvement.
How It Contributes To Exponential Results And Growth:
Interfaces tend to become the most distinctive internal characteristics of a fully realized ExO.
There’s a good reason for this: at peak productivity, Interfaces empower the enterprise’s management of its SCALE external attributes. Without such interfaces the ExO cannot scale, thus making them increasingly mission-critical.
#8 Dashboards
In Short:A real-time, adaptable dashboard with all essential company and employee metrics, accessible to everyone in the organization.
ExO Examples:
In the early 1990s, giant retailers such as Sears and Kmart would calculate their daily transactions store by store. A regional hub then tallies results for multiple stores. Then a buyer at the head office would analyze the total of all regional hubs to determine how many boxes of Pampers the company needs to order for its next bulk purchase. The whole process would take weeks.
Walmart blew this model apart and revolutionized retailing by launching its own real-time dashboard which allowed them to track inventory at any store, instantly. With real-time business information at their fingertips, Walmart could make important decisions quickly and crushed the competition by consistently outperforming other chains by 15 percent — a staggering competitive margin in retail.
How It Contributes To Exponential Results And Growth:
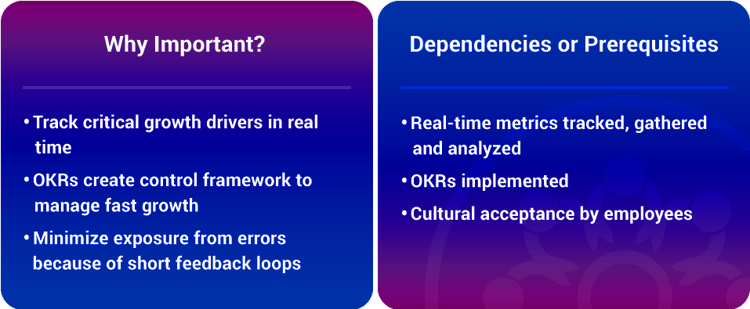
ExOs are growing at a rapid pace. To keep up with this pace, the organization needs to have visibility on all areas of the business. Dashboards which enable visibility allow business, individuals and team assessments to be carried out efficiently and much faster than ever before. Dashboards also allow you to see problems before they grow into big mistakes.
Since tight control frameworks are critical to managing hyper growth, real-time dashboards used in conjunction with defined “Objectives & Key Results” (OKRs) are key. OKRs are about focus, simplicity, short(er) feedback cycles, and openness. As a result, insights and improvements are easier to see and implement.
#9 Experimentation
In Short:The implementation of the lean Startup methodology of testing assumptions and constantly experimenting with controlled risks.
ExO Examples:
Maria Mujica, who heads up the two-year-old innovation unit Fly Garage for Mondelez International, a confectionery company, uses Experimentation to run several-day “Garages” to create new brand engagements.
Groups of free thinkers from inside and outside the organization are invited to participate in a no-boundary environment of these “Garages”, where they:
- Detox by disconnecting and unplugging from everything
- Empathize and immerse so as to connect with the opportunity
- Boil ideas down to a creative brief (brief then transcribed onto a T-shirt that’s worn)
- Agitate to drive ideation and mix/shake up solutions
- Prototype rapidly to enable a fast user experience
How It Contributes To Exponential Results And Growth:
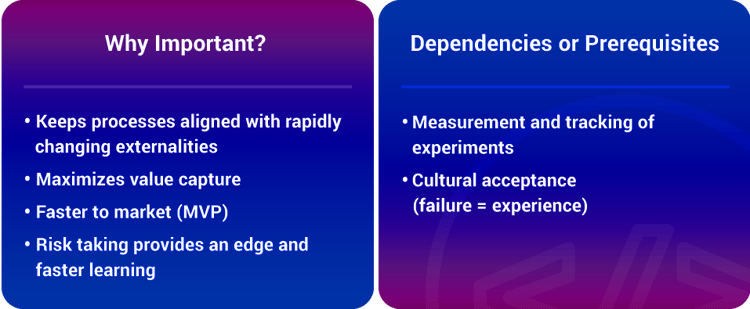
Corporate organization charts are traditionally structured to withstand risk and change. However, in today’s world, the biggest risk is not taking any risk. The modern rule of competition is “whoever learns fastest, wins.”
Experimentation is effectively “scalable learning”. This makes a culture of continuous experimentation even more important. Large numbers of bottom-up ideas, properly filtered, always trump top-down thinking, no matter the industry or organization.
#10 Autonomy
In Short:Self-organizing, multidisciplinary teams operating with decentralized authority.
ExO Examples:
Zappos.com is a company with 4,000 employees which specializes in online retail market for shoes and clothing. The company is uniquely organized around its company culture and core values. In fact, Zappos will pay people to leave if they don’t fit into the company culture.
Additionally, there are no traditional job standards available in Zappos. Instead, the organization encourages their employees to go beyond traditional customer service and their representatives to make decisions on their own.
The financial impact of this autonomy has been huge. In November 2009, Zappos.com was acquired by Amazon.com in a deal valued at $1.2 billion on the day of closing. Gross sales exceeded $1 billion in 2008 (20 percent better than the year before) and 75 percent of its customers are repeat buyers.
How It Contributes To Exponential Results And Growth:
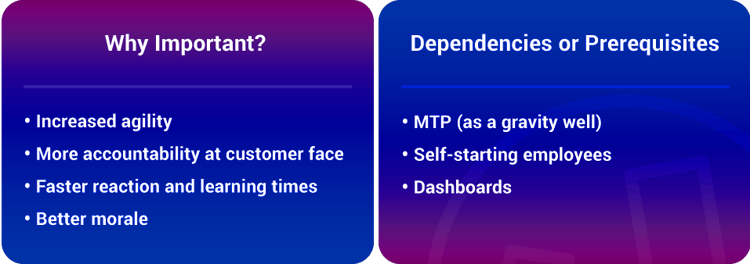
Charles Darwin discovered an interesting aspect about evolution. He found that the fastest progression of evolution did not happen when huge populations were exposed to stressful conditions. In fact, those which evolved the fastest under stressful conditions were small groups of species isolated from the main population.
By the same token, small, independent and interdisciplinary teams are critical to future organizations, especially at the edges.
#11 Social Technologies
In Short:
Social technologies, or collaborative technologies, allows organizations to manage real-time communication amongst all employees. This allows conversations and collaborations between employees to happen easier, faster, and in an organized fashion to facilitate smoother execution of tasks.
ExO Examples: Forrester Research studied one implementation of Microsoft’s Yammer enterprise social network within a 21,000-employee organization. During a payback period of just 4.3 months, and with only one third of the workforce using the product, the company saw an ROI of 365 percent. Given such results, it’s not surprising that Yammer now has 8 million installations.
How It Contributes To Exponential Results And Growth:
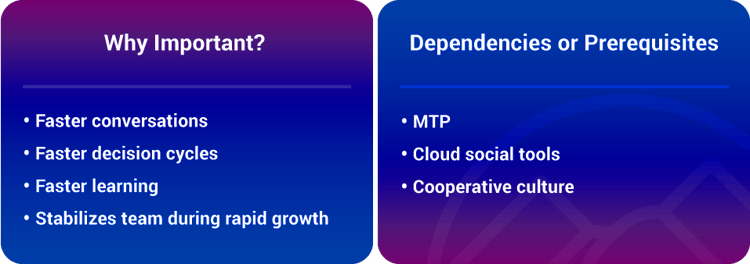
Social Technologies are comprised of seven key elements: Social Objects, Activity Streams, Task Management, File Sharing, Telepresence, Virtual Worlds and Emotional Sensing. When implemented, these elements create transparency and connectedness and, most importantly, lower an organization’s information latency.
The entire social paradigm presents several critical implications for ExOs. Organizational intimacy is increased, decision latency is reduced, knowledge improves and is more widely spread, and serendipity increases. In short, social technologies enable the real-time enterprise.
Scaling Up With These 11 Attributes
For a practical way to learn how to apply this tool into your current business while getting mentorship, peer-to-peer feedback, and customized support as you implement, check out my Exponential Organization Master Business Course here.
Did you find this article on ExOs interesting and useful? Please share your thoughts, comments and questions below!




